Intellectual Property Private Credit (Part 2 of 2)
IP Credit Case Study
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Despite its size, the Intellectual property (“IP”) asset class has eluded the attention of most asset managers due to its underlying legal complexities
Litigation finance industry understands the opportunity, but it is solely focused on litigation involving IP
A void exists in the financing market, which IP-focused Private Credit managers have begun to fill via credit-oriented strategies designed to drive value maximization
INVESTOR INSIGHTS
Secular shifts in the economy have made IP assume an increasing share of corporate value
IP is an emerging asset class that has begun to garner the attention of asset managers and insurers
There are various IP-centric investment strategies that do not involve litigation
IP-focused Private Credit funds approach IP in a holistic fashion, leveraging numerous ways that IP creates value
Investors need to be aware that investing in IP presents unique risks that warrant input from operational and legal IP specialists
IP Credit provides a different risk/reward profile for investors as compared to commercial litigation finance which tends to have more binary risk
In the first part of this two-part series, the relatively nascent asset class of Intellectual Property Private Credit (“IP Credit”) was introduced. That article explored the basic premise of the asset class, discussed some of the financiers in the space and reviewed some of the nuances inherent in the asset class. In this part, we take all of the knowledge gained in part one and apply it to a specific example by exploring a publicly traded company, which used IP Credit on a couple of different occasions with great success.
Case Study
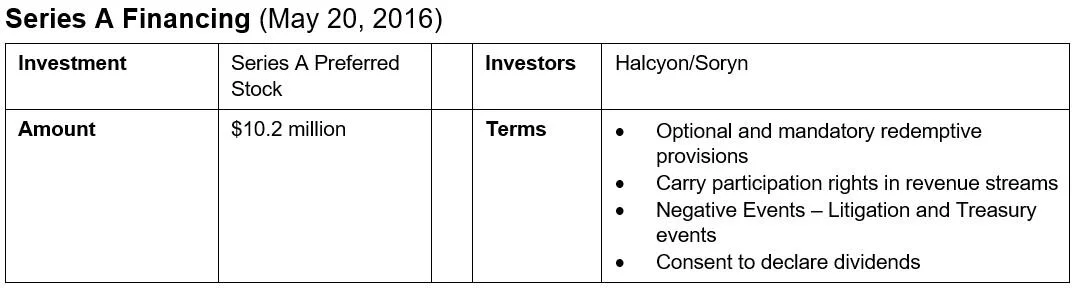
The details of most IP Private Credit transactions remain private. An illustrative exception involves two prior financings of the once publicly traded cybersecurity company Finjan Holdings, Inc. (NASDAQ: FNJN) (“Finjan”), known for its technologies related to proactive cybersecurity. At the time of the financings in 2016 and 2017, Finjan had focused significant effort on the licensing of its patent portfolio — to significant monetary success — in addition to other aspects of its business. But because the licensing of intellectual property often requires costly litigation to complement the negotiation process, Finjan, through its bankers, ran a process to identify a strategic capital partner. Potential proceed uses included litigation and general operating expenses, as well as stock repurchases.
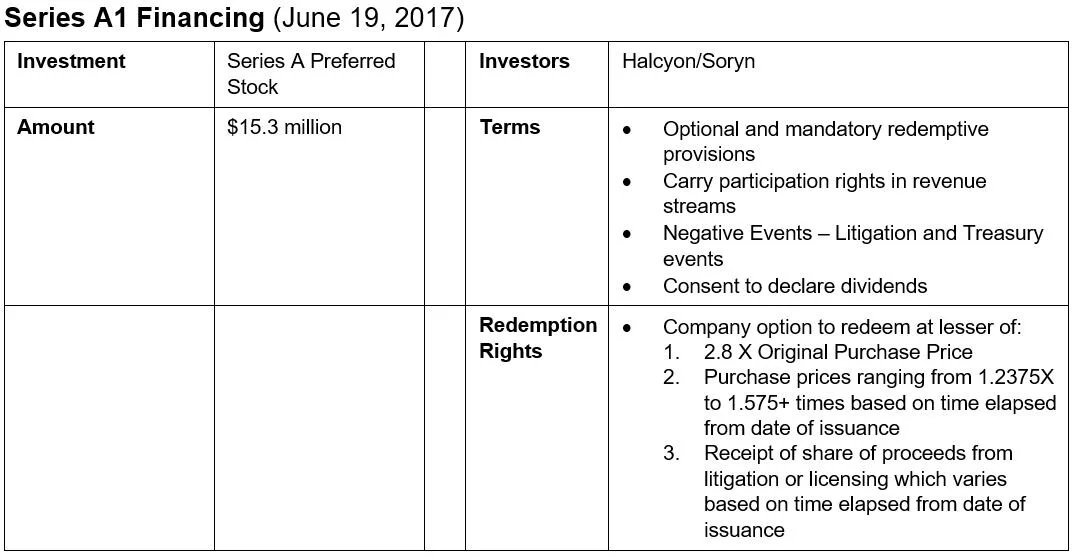
Based on its prior patent licensing success, Finjan likely had numerous traditional, non-recourse litigation financing offers to choose from. But instead of pursuing the litigation finance route, Finjan pursued the IP Credit path. Finjan secured almost $26mm in financing via two, highly structured preferred equity transactions. These transactions featured share redemptions tied to litigation and/or patent licensing revenue events, and also contained “Negative Event” features that entitled the capital partner to recover all of their shares upon the occurrence of certain, pre-agreed negative events. As illustrated in the chart above, the capital partner’s potential returns were capped at multiples ranging from 1.25 to almost 3x the original purchase price of the shares with the range depending mainly on the length of time the capital was outstanding.
Finjan ultimately exited both deals. While the exact motivations behind the deal cannot be known, it is easily theorized that the high structured and downside protected nature of the IP Credit Deal the company ultimately entered into was favorable in a number of respects compared to the higher cost of capital seen in traditional litigation finance arrangements. Finjan was ultimately acquired by Fortress Investment Group in 2020.
Interplay with IP litigation
Of note, and particularly with respect to patents, enforcement litigation is often a necessary tool to resolve licensing disputes or negotiations between IP owners and potential licensees. The reason is that without litigation, a patent owner has no means to force a party that it believes is infringing on its IP to the negotiating table.
Litigation scenarios thus remain part of the broader IP Private Credit strategy. But such litigations can take different shapes and risk profiles. On one end of the risk spectrum are single event litigations, involving a small number of patents, that represent unattractive and binary risk profiles. On the other end of the spectrum are multi venue disputes, involving a significant number of patents, brought by entities owning much larger patent portfolios than what is asserted in litigation.
These types of situations (shown above to the right of the arrow) resemble business negotiations more than binary litigation, and be modeled to resolve in a more predictable fashion. By the nature of a credit-oriented investment strategy, an IP-focused Private Credit fund targets the latter opportunity set, whereas the litigation finance market has shown a willingness to fund what we characterize as the riskier, more binary type enforcement situations.
Accordingly, while litigation is not necessarily an outcome that results from such an investment, a manager that invests in the sector does need to expect, plan and prepare for litigation as a potential outcome or at the very least as a means to an end. The idea, as with most litigation, is that ‘saner heads will prevail’ and that a commercially reasonable settlement will be achieved by both parties prior to embarking on expensive litigation. Of course, this means that the onus is on the investor to understand the merits of the case and the plaintiff’s strategic position, potential defenses, procedural activities that could frustrate or delay litigation, and the costs associated therewith. The complexities associated with understanding the value of intellectual property assets and the complexity of the litigation process make the sector a highly specialized area for investors who are often best served by investing through or alongside specialist managers.
Investor Insights
Secular shifts in the economy should be forcing investors to think about value in different ways. It’s indisputable that intellectual property is clearly the basis for technology company valuations and so value must be attributable to IP when considering financing alternatives. While understanding the value inherent in intellectual property can be difficult, fund managers with specific expertise exist to allow investors to allocate capital in an appropriate risk adjusted manner.
The fact that the insurance industry is now providing insurance products geared toward intellectual property is a testament to how far the industry has come and how significant the opportunity is and perhaps much less risky than one would think, if approached prudently.
I believe the IP Credit asset class has a bright future ahead as existing players have had great success producing consistent returns in a sector that one might otherwise believe to be volatile.
As always, I welcome your comments and counter-points to those raised in this article.
About The Authors
Edward Truant is the founder of Slingshot Capital Inc., and an investor in the consumer and commercial litigation finance industry. Slingshot Capital Inc. is involved in the origination and design of unique opportunities in legal finance markets, globally, investing with and alongside institutional investors.
Soryn IP Capital Management LLC (“Soryn”) is an investment management firm focused on providing flexible financing solutions to companies, law firms and universities that own and manage valuable intellectual property (“IP”) assets. Soryn’s approach employs strategies, including private credit, legal finance, and specialty IP finance, which enable it to invest across a diversity of unique IP-centric opportunities via investments structured as debt, equity, derivatives, and other financial contracts. The Soryn team is comprised of seasoned IP and investment professionals, allowing the firm to directly source opportunities less travelled by traditional alternative asset managers.
INFORMATION SOURCES
IP-Based Financing of Innovative Firms (OECD) https://www.oecd.org/sti/ieconomy/Chapter9-KBC2-IP.pdf
Financial Development (World Bank) https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/gfdr/gfdr-2016/background/financial-development
The Puzzle in Financing with Trademark Collateral https://www.law.uh.edu/ipil/symposium/prior/2018/6778-the-puzzle-in-financing-with-trademark-collateral.pdf
Patent Aversion: An Empirical Study of Patents Collateral in Bank Lending (1980-2016) https://www.law.uci.edu/lawreview/vol9/Online_Nguyen.pdf
Insurers are Credit Facilitators https://www.iii.org/sites/default/files/docs/pdf/insurance-driver-econ-growth-053018.pdf
Asset Based Lending: IP https://www.appraisaleconomics.com/asset-based-lending-intellectual-property/
The Role of Insurance in Ensuring Financial Market Liquidity https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1111%2F1468-0440.00120.pdf
Maximizing Intellectual Property and Intangible Assets https://www.issuelab.org/resources/3304/3304.pdf
Private Credit Strategies (Cambridge Associates) https://caia.org/sites/default/files/0._private_credit_strategies_an_introduction.pdf
Types of Intangible Assets (ITR) https://www.internationaltaxreview.com/article/b1fyg9wg61n4m9/intangible-assets-in-the-media-and-entertainment-industries-in-depth-analysis
The Intellectual Property (IP) Audit: An Effective IP Asset Management Tool (Strook) https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0883911503008001011
Sanctions for Trade Secret Thieves Part of Senate-Passed Bill (Bloomberg) https://news.bloomberglaw.com/ip-law/sanctions-for-trade-secret-thieves-part-of-senate-passed-bill
Intellectual Property Theft/Piracy (FBI Website) https://www.fbi.gov/investigate/white-collar-crime/piracy-ip-theft
Financial Development (World Bank) https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/gfdr/gfdr-2016/background/financial-development
The Decline of Secured Debt (NBER) https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w26637/w26637.pdf
A Century of Capital Structure: The leveraging of Corporate America http://finance.wharton.upenn.edu/~mrrobert/resources/Publications/100YearsJFE2015.pdf
Why Did Universities Start Patenting (Social Studies of Science, Dec 2008) https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306312708098605
Intellectual Property and the US Economy (USTPO) https://www.uspto.gov/learning-and-resources/ip-motion/intellectual-property-and-us-economy